Human papillomavirus (HPV) causes the growth of skin epithelium, anogenital mucosa, and upper respiratory tract. It most commonly affects the internal organs — the esophagus, the bronchi, the rectum, and the bladder. As a result of the activity of the virus, various forms of tumors appear. Some of them are very benign, and some carry the risk of cancer. In what cases does papilloma require special attention and removal? This is stated in the article.
The route of infection
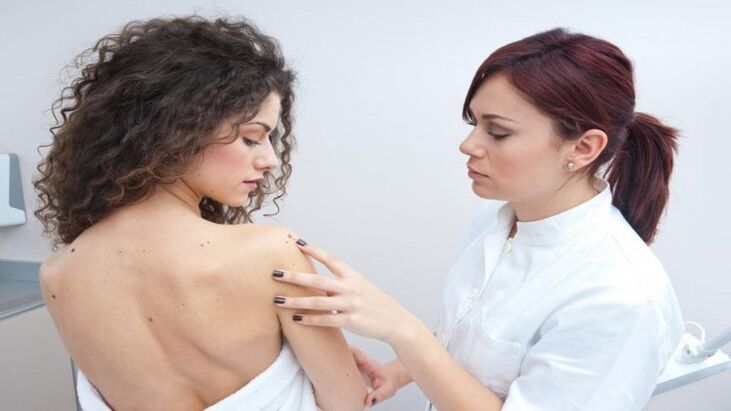
Infection occurs after contact with a carrier of the virus, as well as an infected person or animal. It should be noted that the patient may have no clinical manifestations of papillomatosis. Sometimes he doesn't even know about the infection. The virus enters the human body through the microbes of the skin or mucous membranes. Only viral particles are sufficient for the development of the infectious process. The virus can maintain its viability in the environment. Therefore, self-infection is possible during hygienic procedures and daily life (shaving, epilation, skin combing, self-injection). Bath, swimming pool, gym, etc. A newborn baby can become a carrier of human papillomavirus infection when it passes through the mother's birth canal.
Types of HPV
To date, researchers have identified about 180 types of HPV, 29 of which are oncogenic. Depending on the oncogenic potential, viruses are divided into:
- low level of oncoactivity (types 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81),
- average level of oncoactivity (types 26, 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 53, 58, 66)
- high levels of oncoactivity (16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82).
According to the latest data, one or another strain of human papillomavirus is found in the blood of about 80% of the world's population. However, this does not mean that all patients have papillomatosis. What factors contribute to the development of the disease?
Immunity and papilloma
Why does the virus disappear from the body of some people, persist for the rest of their lives, and cause papillomas in others? HPV is an infection that can suppress the immune system. Healthy people and carriers of the virus have a strong immune system that suppresses the growth of foreign agents. The special role of cellular immunity has been confirmed. At its level, it blocks the persistence of the virus (the ability to activate it over a long period of time, except in the acute phase), and in some cases promotes regression of wounds. Spontaneous regression of papillomatosis occurs within six months. However, not everyone's immune system is at such a high level, and latent HPV infection becomes manifest. Papilloma occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- perverted sex life, frequent change of partners;
- contact with a partner with a history of sexual papillomatosis;
- presence of sexually transmitted infections during pregnancy;
- immune deficiency in vitamin deficiency, atopic dermatitis, pregnancy, AIDS;
- frequent colds and SARS;
- hormonal contraception;
- autoimmune diseases;
- tobacco and alcohol.
The skin, which has a tendency to become damaged or inflamed, becomes a strong provocative factor, which stops it from performing its protective function. Therefore, people with inflammatory skin diseases (acne, rashes), eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis are at risk.
Papillomatosis of the respiratory system
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is the most common benign tumor of the larynx. Respiratory papillomas can occur in any area - from the nasopharynx to the lung parenchyma. However, it usually attacks the mucous membranes of the larynx. The severity of the disease is determined by the presence of obstruction in the narrowest area, the presence of pre-asphyxia. In adults, the obligate is considered a precursor due to the high incidence of cancer (necessary tumor growth). The main symptom of the disease is usually a loss of volume. The patient can speak in a whisper. In the first stage, the appearance of respiratory papillomatosis is sometimes confused with acute laryngitis. Therefore, it is impossible to prescribe treatment without endoscopic examination. Various physiotherapy procedures in the larynx lead to the rapid growth of papillomas.
Children's warts
Warts are benign growths of the epidermis that are found mainly in children and adolescents. They develop on the face, arms, and neck and often cause many emotional problems to their owners. However, more than 70% of these types of papillomas disappear without a trace in 1, 5 - 2 years. Therefore, doctors only resort to removing them in very severe cases, because once the hormonal changes are complete, the body may be able to fight HPV infection on its own. Additional risk factors in childhood include frequent stress related to study and exams, overwork, lack of sleep, poor nutrition, sensitive baby skin, and acne in adolescents.
Should papilloma be removed from the skin
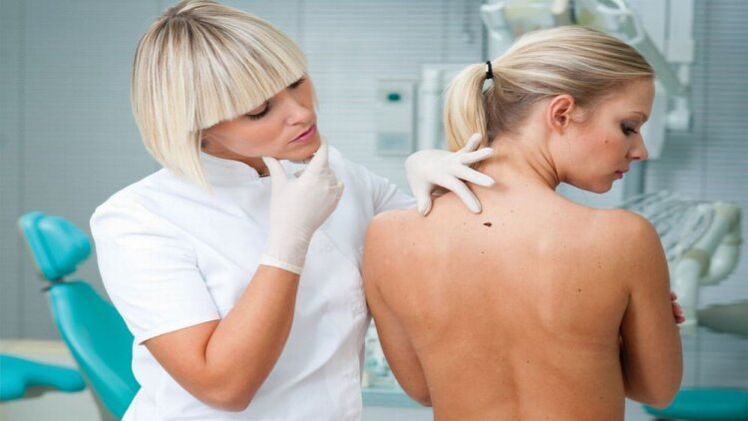
Some tumors are malignant. This process cannot be ignored if one pays attention to oneself. If one of the signs is found, an alarm must be given:
- The size and configuration of the papilloma changes (it grows rapidly, the edges are blurred, additional growths and fillings appear);
- the color of the new tumor changes as it darkens;
- The inflammatory process is added, the skin peels, cracks, exudate flows;
- The disease occurs.
All of the above are indicators to eliminate growth. It is also worth resorting to a radical approach to solving problems if the papilloma is located at the site of daily trauma (neck, armpit, lumbar region, etc. ). Regular grazing and mowing can trigger the oncological process and also promote the entry of pathogenic microorganisms.
Methods of eliminating tumors
Destructive treatments for skin growth are divided into:
- chemical (trichloroacetic acid 80-90% and other drugs);
- physical (plasma coagulation, cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrosurgery).
If removal is expected in adolescents or pregnant women, only laser therapy is used. After destruction, the use of local antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs is indicated.
The main method of eliminating laryngeal papillomas is endolaryngeal surgery under anesthesia using micro-instruments or a surgical laser, followed by permanent remission in only one-third of patients. In practice, a combined approach is used: additional cryodestruction is performed (with the local form of the disease), local anti-tumor drugs are prescribed. The most common is inhalation with a special solution.














































































